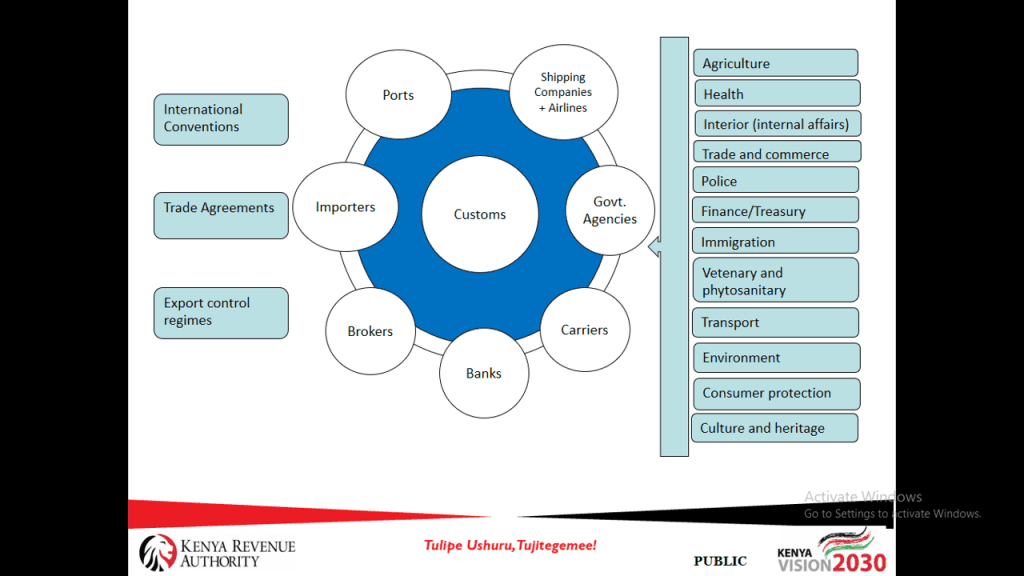
Customs Organs and Institutions
The World Customs Organization
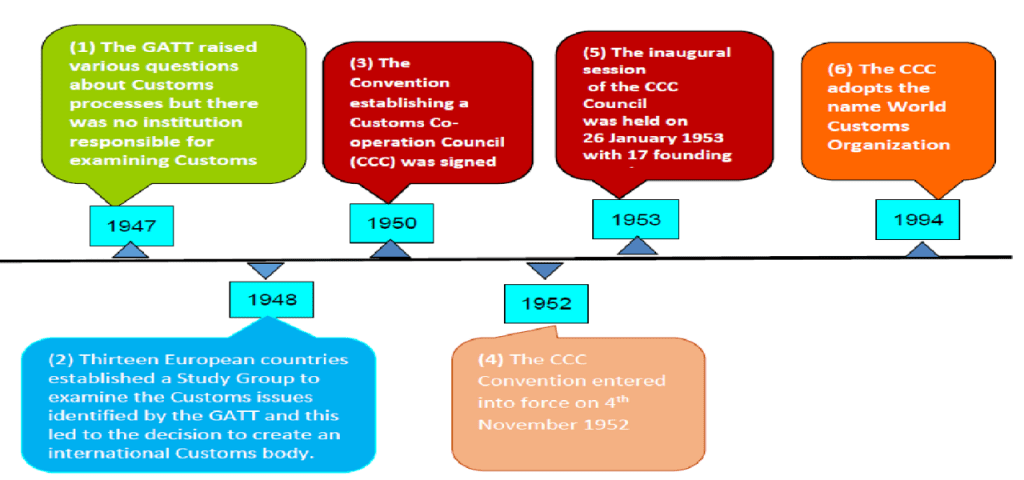
- The World Customs Organization (WCO) was established in 1952 as the Customs Cooperation Council.
- It is an independent intergovernmental body whose aim is to enhance effectiveness and efficiency of Customs Administrations. Currently, the WCO has 183 Member countries that process approximately 98% of the world’s trade.
- All the East African Partner States – Kenya, Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi and South Sudan- are Members of the WCO.

The WCO Roles
- Develops international standards,
- Fosters cooperation and builds capacity to facilitate legitimate trade, to secure a fair revenue collection and to protect society,
- Provides leadership, guidance and support to customs administrations.
The organization’s structure consists of:
- The Council – It is the supreme decision-making body of the WCO and convenes once a year. All Member States are represented in the Council.
- Policy Commission- The Policy Commission submits policy recommendations and the WCO Strategic plan to the Council. It comprises of thirty members and it meets twice a year.
- Finance Committee- It provides support and advice to the Policy Commission and Council in budgetary and financial matters. It comprises of seventeen Members and meets once a year.
- Audit Committee- Its responsibility is to undertake management audits. It comprises of six Members and meets once a year.
- The WCO Secretariat comprises of:
- The Secretariat- The WCO headquarters are in Brussels, Belgium. The Secretariat staff assist in running daily operations of the organization, under the leadership of the Secretary General.
- The Secretary General- He provides leadership and executive management for the global Customs community’s priorities.
iii. The Directorates- There are three Directorates in the WCO:
- Tariff and Trade Affairs Directorate (responsible for classification, valuation and rules of origin matters);
- Compliance and Facilitation Directorate (responsible for compliance, enforcement, procedures and trade facilitation matters);
- Capacity Building Directorate (responsible for coordinating and delivering capacity building, technical assistance and training to WCO Members).
WCO Working Bodies
- Harmonized System Committee;
- Technical Committee on Customs Valuation; Technical Committee on Rules of Origin;
- Enforcement Committee;
- Permanent Technical Committee;
- Capacity Building Committee;
- Integrity Sub-Committee;
- Private Sector Consultative Group.
The East African Community
Article 9 of the Treaty on Establishment of the EAC provides for the following organs of the community:
- The Summit- It consists of the Heads of State who give general directions and impetus as to the development and achievement of the objectives of the Community.
- The Council- It consists of the Ministers responsible for East African Community Affairs of each Partner State; Minister of the Partner States as each Partner State may determine; and the Attorney General of each Partner State. The council is the policy organ of the Community.
- The Coordination Committee- It consists of the Permanent Secretaries responsible for East African Community affairs in each Partner State and such other Permanent Secretaries of the Partner States as each Partner State may determine.
- Sectoral Committees- This Committees are responsible for preparation of comprehensive implementation programmes; monitoring of the implementation; and making recommendations to the Coordination Committee concerning the implementation.
- The East African Court of Justice- This is a judicial body which ensures the adherence to law in the implementation and application of and compliance with the Treaty.
- The East African Legislative Assembly- It comprises of nine members elected by each Partner State; and ex-officio members consisting of:
- the Minister responsible for the EAC affairs from each Partner State;
- the Assistant Minister/ Deputy Minister/ Minister of State responsible for East African Community affairs from each Partner State; and
- the Secretary General and the Counsel to the Community.
- The Secretariat- This is the executive organ of the Community which consists of the Secretary General, the Deputy Secretaries General; the Counsel to the Community; and such other offices as may be deemed necessary by the Council.
Customs Administrations in the Partner States
- The four main roles of Customs Administrations globally include
- Trade facilitation;
- Revenue collection;
- Protection of society;
- Collection of national statistics.
- The focus of Customs with regard to its roles has been evolving over the years as shown in the diagram below:
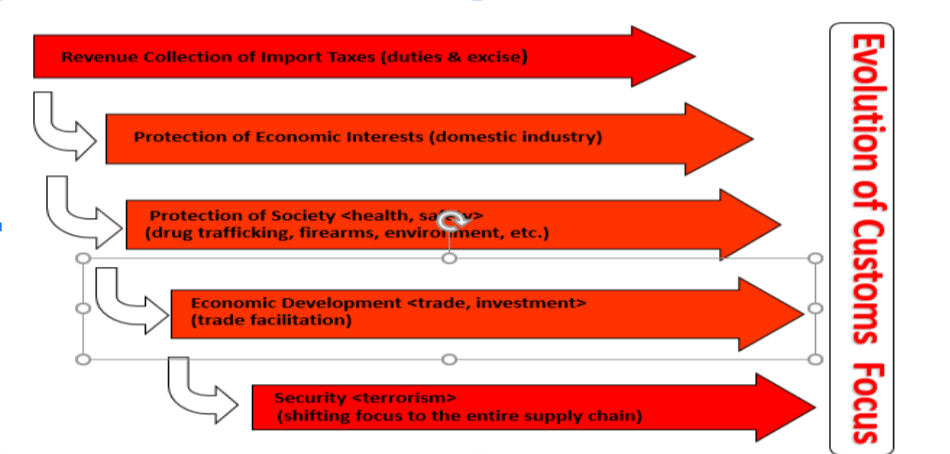

Role of Customs Administrations in Cargo Clearance