Types, sources and functions documents in Freight Forwarding
Types, sources and functions documents in Freight Forwarding
Documents can be mainly divided into three categories;
- Documents related to the sale of goods – commercial invoice, Pro-forma invoice, quotation, bill of quantity, letter of credit, bill of exchange, consular invoice
- Documents related to the transport of goods- bill of lading, airway bill, packing list, consignment notes, multimodal transport documents, shipping order, mate’s receipts, stowage order/plan, loading/discharging receipts, cargo manifest, charter party agreement, MDG/IATA/FIATA declaration of dangerous goods form, delivery order
- Other Documents – certificate of conformity, certificate of origin, donation certificate, customs entry etc
Documents Related to The Sale of Goods
Pro-forma Invoice
- A pro forma invoice is a preliminary bill of sale sent to buyers in advance of a shipment or delivery of goods.
- It describes the items and other important information such as the kind of goods, quantity, their value, and other important information such as weight and transportation charges.
- Pro forma invoices are commonly used as preliminary invoices with a quotation, or for customs purposes in importation.


Commercial Invoice
- It is a document required by customs to determine true value of the imported goods, for assessment of duties and taxes.
- A commercial invoice (in addition to other information), must
- Identify the buyer and seller,
- Clearly indicate the date and terms of sale, quantity, weight and/or volume of the shipment,
- Type of packaging,
- Complete description of goods,
- Unit value and total value,
- Insurance,
- Terms of delivery and payment,
- Vessel/flight details,
- Port/airport of discharge,
- Place of delivery, shipping and other charges (as applicable).


Consular Invoice
- It is an invoice that describes the goods being transported.
- The exporter authenticates the accuracy of the invoice by appearing before the Importer Country’s Consul who is stationed in the exporter’s country.
Quotation
- This is an inquiry regarding the price and quantity of goods and services. It also includes the terms of payment and delivery.
- It also gives a range of product items and hence the time of supply is not fixed.
Bill of quantity (BOQ)
- This document is a full list of items, quantity and value of the items to be delivered for projects.
Letter of Credit
- A letter of credit (LC) also known as a documentary credit or bankers’ commercial credit, is a payment mechanism used in international trade to provide an economic guarantee from a credit worthy bank to an exporter of goods.
- A letter of credit is issued by a bank to another bank (especially one in a different country) to serve as a guarantee for payments made to a specified person under specified conditions.
Purpose of Letters of Credit
- The purpose of this document is to reduce credit risk to sellers in both domestic and international sales arrangements. By having a bank issue a letter of credit, in essence, one is substituting the bank’s credit worthiness for that of the customer.
Types of Letters of Credit
- There are two basic forms of letters of credit:
- Standby
- Documentary.
Documentary Letters of Credit
- Documentary letters of credit can be either Revocable or Irrevocable, although the first is extremely rare.
- Irrevocable letters of credit can be Confirmed or Not Confirmed.
Documentary Revocable Letter of Credit
- Revocable credits may be modified or even canceled by the buyer without notice to the seller. Therefore, they are generally unacceptable to the seller.
Documentary Irrevocable Letter of Credit
- This is the most common form of credit used in international trade. Irrevocable credits may not be modified or canceled by the buyer.
- The buyer’s issuing bank must follow through with payment to the seller so long as the seller complies with the conditions listed in the
Documents Related to The Sale of Goods
There are two forms of irrevocable credits:
- Unconfirmed credit
- Confirmed credit (the irrevocable confirmed credit)
Standby Letter of Credit
- This credit is a payment or performance guarantee
- Often called non-performing letters of credit because they are only used as a backup should the buyer fail to pay as agreed.
- A stand-by letter of credit allows the customer to establish a rapport with the seller by showing that it can fulfill its payment commitments.
- Standby letters of credit are used, for example, to guarantee repayment of loans, to ensure fulfillment of a contract, and to secure payment for goods delivered by third parties.


Bill of Exchange (BoE):
- A Bill of Exchange is legally defined as an ‘unconditional’ order in writing addressed by one person to another, signed by the person giving it, requiring the person to whom it is addressed to pay on demand or at a fixed or determinable future time a certain sum in money to or to the order of a specified person, or bearer.
- The Bill of Exchange looks something like a cheque and is prepared by the exporter and drawn on an overseas buyer, or even a third party, as designated in the export contract for the sum agreed as settlement.
- By using a Bill of Exchange with other shipping documents through the banking system, an exporter can ensure greater control of the goods, because until the Bill of Exchange is paid or accepted by the overseas buyer the goods cannot be released.
Documents Related to Transport of Goods
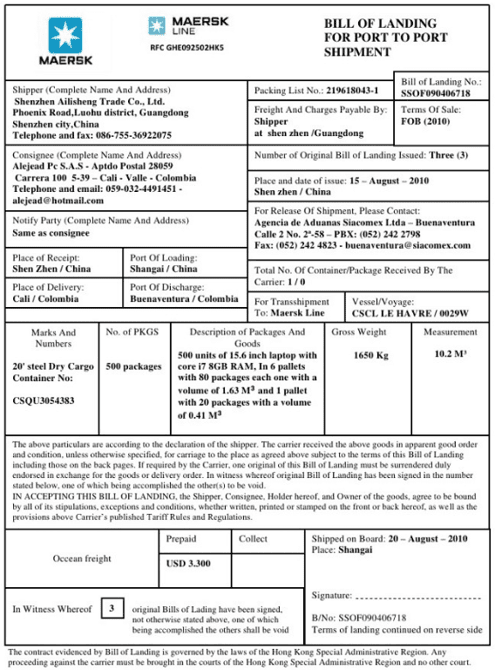
Bill of Lading (B/L)
- A bill of lading (B/L) is a legal document issued by a carrier to a shipper that details the type, quantity, and destination of the goods being carried.
- A bill of lading also serves as a shipment receipt when the carrier delivers the goods at a predetermined destination.
- This document must accompany the shipped products, no matter the form of transportation, and must be signed by an authorized representative from of the carrier.
- The word “lading” means “loading”, it specifically refers to the loading of cargo aboard a ship.
Information on Bill of Lading
- Name of the Shipping Company/Carrier that has issued it.
- Shipper’s full style address/details (Usually the exporter).
- Name and Address of the Importer/Consignee or Order.
- Name and address of the Notify Party (The person to be notified on arrival of goods at destination-usually the importer or agent).
- Name of the carrying vessel and voyage details.
- The names of the Port of Loading/Port of destination.
- The Marks and numbers identifying the cargo.
- A brief description of the goods, possibly including weights and dimensions.
- The shipping terms, CIF, FOB, and Freight collect or Pre-paid.
- The number of original documents printed; all retained at origin port or retained by the carrier in this case a T.R will prevail.
- The signature of the shipper or his agent.
- The date on which the goods were received for shipment/ Date cargo was shipped on board.

Functions of a Bill of Lading
- It is the carrier’s receipt for carriage of goods by sea. It therefore has several functions:
- The issuance of a Bill of Lading by the carrier is a proof that the goods have been received from the shipper or their agent in a apparent good order and condition as handed over by the shipper.
- A bill of lading issued by the carrier or their agent to the shipper or their agent as proof of receipt of the cargo
- A bill of lading is an acknowledgement of receipt of goods specified in it (in its free space known as the margin)
- A bill of lading is a prima facie evidence or conclusive evidence of facts contained in it as stated by the shipper
Forms of Bills of Lading
- Combined transport bill of lading: Also known as port-to-port bill of lading.
- Order bills of lading: These have no named consignee, the word “order” being inserted in the “consignee” box while the intended consignee is shown as a “notify party” immediately underneath.
- Through bills of lading: A through bill of lading is used when goods are being transshipped. It covers both legs of the journey.
- Cover bills of lading: Where cargo is short-shipped from an earlier consignment (sometimes by accident, the cargo being left in a shed in error) it has to be sent on by the first available ship.
- Clean, dirty and stale bills: Bills of lading may be clean, dirty or stale.
Forms of Bills of Lading
- Sea waybill is a non-negotiable document that also functions as a receipt for shipment and as evidence of the contract of carriage.
- House bills of lading: With the development of consolidation/groupage by sea consequent upon containerization, the house (or forwarding agent’s) bill of lading is increasing in importance..
- Non-negotiable bills of lading: Also referred to as Straight bill of lading.
Air Waybill (AWB)
- An air waybill (AWB) is a document that accompanies goods shipped by an international air carrier to provide detailed information about the shipment and allow it to be tracked.
- An air waybill (AWB) serves as a receipt of goods by an airline (the carrier), as well as a contract of carriage between the shipper and the carrier.
- It’s a legal agreement that’s enforceable by law.
Functions of an airway bill
- Evidence of receipt of goods by the carrier
- Contract of carriage of goods by air
- Freight bill
- Certificate of insurance
- Customs declaration
- A packing list is a document that includes details about the contents of a package.
- The packing list is intended to let transport agencies, and customers know the contents of the package.
- These details help each of these parties handle the package accordingly.
- It also allows the customer and others involved in the transaction to check what has been shipped against the package contents.


Stowage Plan:
- This is a plan depicting location of cargo stowed in ship or unit of carriage.
- To the exporter or shipper, it is paramount he/she is aware of the principle of cargo stowage, particularly in an era where more shippers are stuffing containers or operating their own TIR international haulage vehicle or inter-modal service.
- The prime consideration is the safety of the transport unit employed which may be a container, vessel, aircraft or road vehicle.

Stowage Order:
- A document issued by the ship-owner indicating acceptance of a specified cargo on a particular ship sailing from a port and featuring the ship owner’s reference.
- It is usually associated with the movement of dangerous classified cargo by sea.
- The stowage order will indicate where the cargo is to be stowed on the ship.
- The master has the right to refuse to ship dangerous cargo if the circumstances warrant such a decision.
Mate’s Receipts:
- This is a document issued to the shipper for ship’s cargo loaded from lighterage and later exchanged for Bill of Lading.
- Also known as the Standard Shipping Note (SSN)
- Mate’s Receipt is a receipted lighterage note evidencing shipment on board of goods delivered by lighter or barge to a vessel.

Cargo Manifest
- A shipping document used by customs personnel reviewing a particular transport vessel’s intended trip that summarizes all bills of lading that have been issued by the carrier or its representative for that particular shipment.
- For example, a cargo manifest might be used for shipments made by sea, air or land, and will generally show the shipment’s cosigner and consignee, as well as listing product details such as number, value, origin and destination.
Delivery Order (D/O)
- A delivery order (abbreviated D/O) is a document from a shipping carrier instructing a terminal operator or shipping agent to release cargo or freight to the agent or consignee designated on the Bill of Lading.
- This document is required by the agent or consignee to clear the goods through customs and marks the end of the transport contract between the shipping carrier and consignee.
- A delivery Order gives details of imported goods that are to be delivered to a consignee or agent by a port authority.


Cargo Arrival Notice:
- An (Air) Cargo Arrival Notice is a letter of advice and request to the consignee, issued only when the client has failed to contact the airline regarding the processing of the imported goods.
- Source of document: Airline e.g. Kenya Airways; or IATA Air Freight agent.
- It is used to inform the consignee of the arrival of the goods at the specified airport; and to request the appropriate documents to enable the consignment to be cleared through customs.
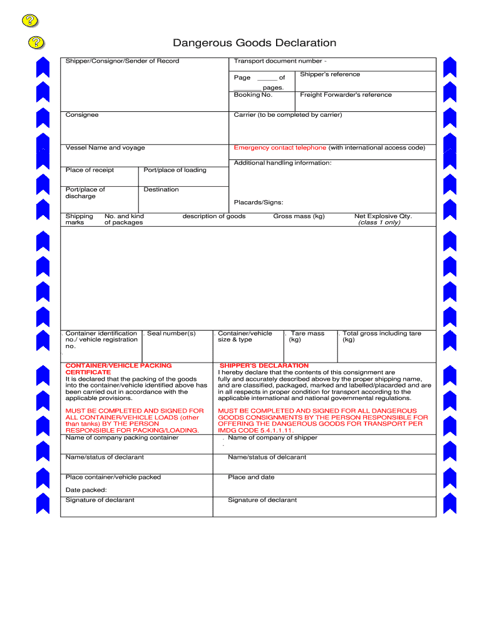
MDG/IATA/FIATA declaration of dangerous goods form:
- The shipper’s declaration for dangerous goods together with an Airway Bill of lading MUST accompany a consignment of dangerous classified cargo on each occasion when it is dispatched by air.

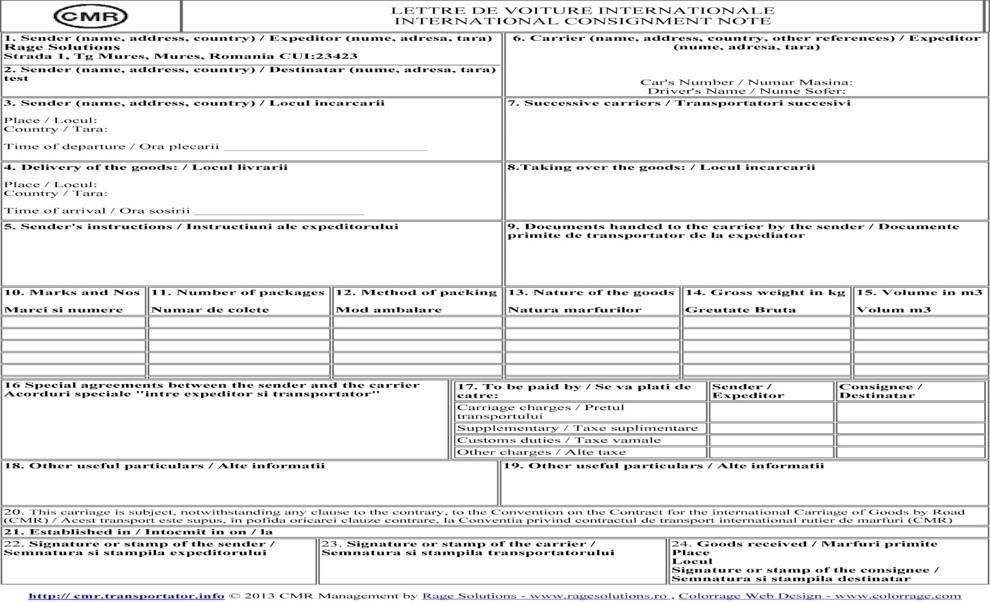
Road Consignment Note (CMR)
- Road consignment note is a document with details of goods sent from a seller to a buyer by road, and that travels with the goods.
- The road consignment note confirms that the haulage company has received the goods.
- It is prepared by a consignor and countersigned by the carrier as a proof of receipt of consignment for delivery at the destination.
- Used as an alternative to bill of lading (specially in inland transport), it is generally neither a contract of carriage nor a negotiable instrument (document of title)

Other Documents
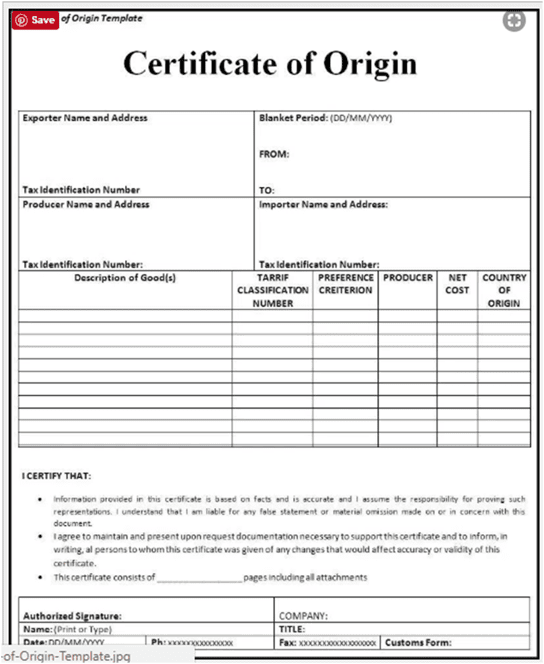
Certificate Of Origin (COO)
- A Certificate of Origin (COO) is an important international trade document that certifies that goods in a particular export shipment are wholly obtained, produced, manufactured or processed in a particular country.
- The certificate contains information regarding the product, its destination, and the country of export, it is widely used in international transactions which attests that the product listed therein has met certain criteria to be considered as originating in a particular country.
- A certificate of origin is generally prepared and completed by the exporter or the manufacturer, and may be subject to official certification by an authorized third party.

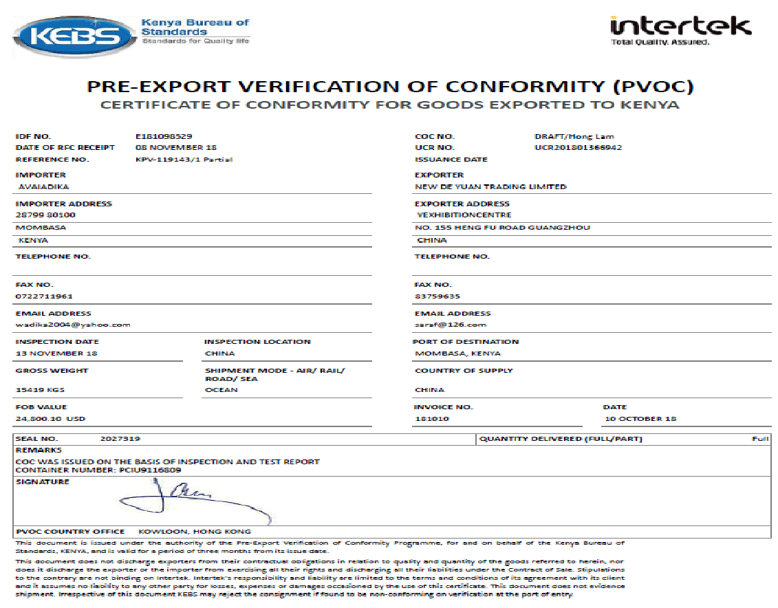
Certificate of Conformity
- A document certified by a competent authority that the supplied goods or services meet the required specifications.
- Also called certificate of conformance or certificate of compliance.
- It is document given to exporters or importers to show that the goods or services bought or supplied meet the required standards.

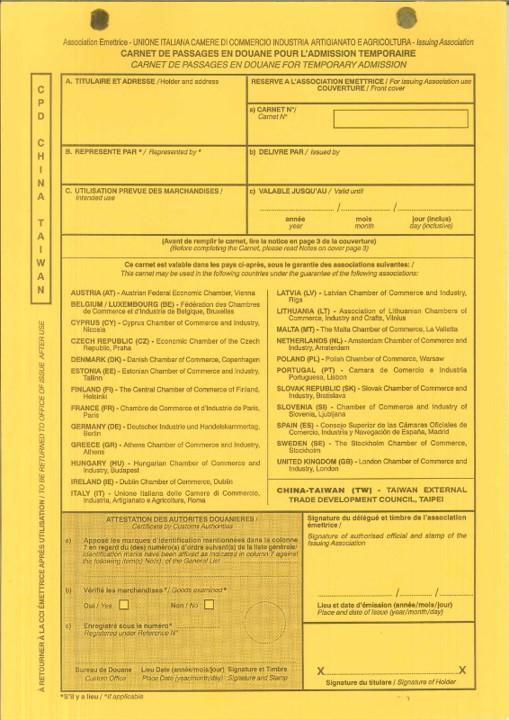
Carnet
- The Carnet often referred to as the “Passport for goods” or “Merchandise passport”, is an international customs document that permits the tax-free and duty-free temporary export and import of nonperishable goods for up to one year.
- It consists of unified Customs declaration forms which are prepared ready to use at every border crossing point.
- It is a globally accepted guarantee for Customs duties and taxes which can replace security deposit required by each Customs authorities.
- It can be used in multiple countries in multiple trips up to its one-year validity.

Donation Certificate
- Donation Certificate, is a document which is used as a way to transfer property well within an owner’s lifetime, and without any monetary consideration.
Insurance Document
- To protect goods in transit from loss or damage from the time they leave the exporter’s warehouse and until they reach the importer’s warehouse, the goods are insured by the importer.
Charter party:
- A charter party is a document under which a vessel is hired or chartered. There are basically two types of charter party; demise and non-demise.
- In a demise (or bareboat) charter, the charterer takes responsibility for the crewing and maintenance of the ship during the time of the charter.
- The charter party serves as a contract whereby a ship-owner agrees to place the ship, or part of it, at the disposal of a merchant or other person (known as the charterer), for the carriage of goods from one port to another port on being paid freight, or to let the ship for a specified period, the ship owner’s remuneration being known as “hire money”.

Learning Activities
Identify three types of documents for transportation of goods and discuss how they are used in clearing of cargo at various entry points.
Assignment
- Explain the functions of a sea way bill
- Explain the use of the following documents
- Pro-forma invoice
- Certificate of donation
- Customs entry
