Topic 1,
Sub-Topic 1
In Progress
Customs Instruments – Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC), 1999
Customs Instruments - Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC), 1999
- RKC is an international agreement that provides a set of comprehensive Customs procedures to facilitate legitimate international trade while effecting Customs controls including the protection of Customs revenue and society.
- The RKC is the blueprint for modern and efficient Customs procedures in the 21st century.
- It is the main Customs facilitation instrument of the WCO.
- RKC is also referred to as “International Convention on the Simplification and Harmonization of Customs Procedures (as amended)”. The preceding Convention is the “Kyoto Convention” which was adopted in 1973 at the WCO Council Sessions in Kyoto, Japan and entered into force in 1974. The Protocol of Amendment to the 1973 Convention was adopted in 1999 and entered into force on February 3rd, 2006.
Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC), 1999
It deals with the following key principles:
- Transparency and predictability of Customs actions;
- Standardization and simplification of the goods declaration and supporting documents;
- Simplified procedures for authorized persons;
- Maximum use of information technology
- Minimum necessary Customs control to ensure compliance with regulations;
- Use of risk management and audit based controls;
- Coordinated interventions with other border agencies;
- Partnership with the trade.
The structure of the RKC consists of:
- The full text of the body of the Convention;
- The General Annex;
- The Specific Annexes relating to specific Customs procedures and practices;
- Guidelines to the Specific Annexes.
Benefits of the RKC to the Partner States’ economies include:
- Reduced transaction costs and avoidance of delays in the release and clearance process
- Increased economic competitiveness
- Promotion of foreign direct investment and development of industry
- Increased participation of small and medium-sized enterprises in international trade
- Lower costs to consumers
- Increased national revenue
Benefits of the RKC to the Trade Community include:
- Faster, predictable and efficient Customs clearance
- Transparent procedures and appeals procedure
- Greater facilitation for compliant traders
- Lower compliance costs
- Enhanced competitiveness
- Use of Information Technology
- Benefits of the RKC to Partner States’ Customs Administrations include:
- Enhanced Customs controls
- Increased trade facilitation
- More effective and efficient deployment of Customs resources
- Reduced integrity problems
- Enhanced supply chain security
World Trade Organization- Facilitation Agreement
- Trade facilitation is the simplification and harmonization of international trade procedures, which include activities, practices and formalities involved in presenting, collecting, communicating and processing data required for movement of goods in international trade.
- Trade facilitation simply means the avoidance of unnecessary trade restrictiveness.
- The WTO is an intergovernmental organization that deals with global rules of trade between nations. Its main objective is to ensure that trade flows smoothly, freely and predictably.
- WTO members concluded negotiations at the 2013 Bali Ministerial Conference on the landmark Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA), which entered into force on 22 February 2017 following its ratification by two-thirds of the WTO membership.
WTO TFA Development Milestones
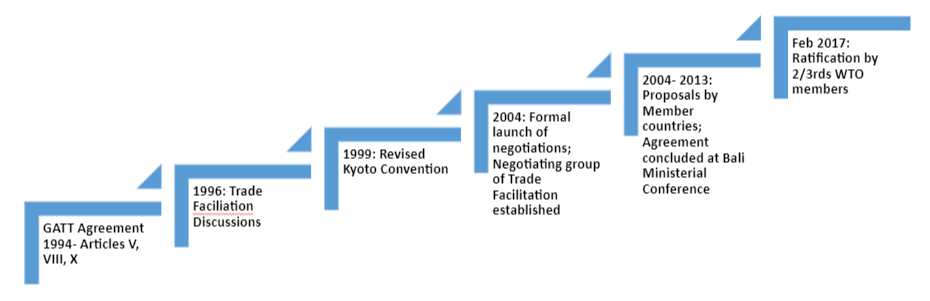

WTO TFA
- The TFA contains
- Provisions for expediting the movement,
- Release and clearance of goods, including goods in transit.
- Measures for effective cooperation between customs and other appropriate authorities on trade facilitation and customs compliance issues.
- Provisions for technical assistance and capacity building in this area
WTO TFA Structure
- Section I
- Twelve articles regarding Trade Facilitation and Customs Cooperation.
- Section II
- Ten articles on Special and Differential Treatment for Developing Countries and Least-Developed Countries
- Section III
- Two articles on Institutional Arrangements and Final Provisions
WTO TFA Impacts
- It is expected that the WTO TFA will have the following impact on the Partner States:
- Reform of national procedures to ease trade and reduce red tape
- Significant economic benefits in terms of added export potential
- Increased foreign investment
- Access to wider range of goods to customers
- Reduce total trade costs by at least 14% for low-income countries and more than 13% for upper middle income countries
WCO SAFE Framework of Standards
- This Framework of Standards was developed by the WCO to secure and facilitate global trade by helping international trade stakeholders to cooperate more effectively in order to improve supply chain security.
- The Standards serve as thresholds of what must be done by WCO Members.
- The SAFE Framework aims to:
- Establish standards that provide supply chain security and facilitation at a global level to promote certainty and predictability.
- Enable integrated and harmonized supply chain management for all modes of transport.
- Enhance the role, functions and capabilities of Customs to meet the challenges and opportunities of the 21st Century.
- Strengthen co-operation between Customs administrations to improve their capability to detect high-risk consignments.
- Strengthen co-operation between Customs administrations, for example through exchange of information, mutual recognition of controls, mutual recognition of Authorized Economic Operators (AEOs)2, and mutual administrative assistance.
- Strengthen co-operation between Customs administrations and other Government agencies involved in international trade and security such as through Single Window.
- Strengthen Customs/Business co-operation.
- Promote the seamless movement of goods through secure international trade supply chains.
Pillars of the WCO SAFE Framework of Standards
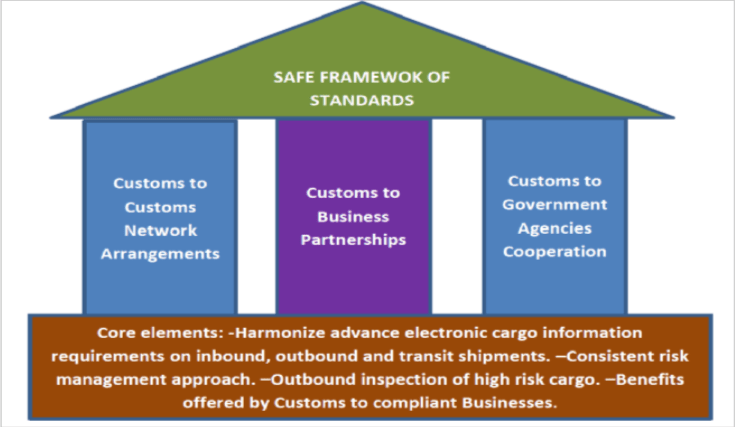

WCO SAFE Framework of Standards Benefits
Benefits to Governments
- Promote the seamless movement of goods through secure international trade supply chains, thus securing trade against terrorism and other transnational crimes;
- Enhanced international trade will contribute to economic growth and development;
- Modernization of Customs operations which will result to improved revenue collection and proper application of national laws and regulations;
- Enable economic and social protection;
- Improve foreign direct investment.
Benefits to Customs
- Exchange of timely and accurate information that will place Customs administrations in the position of managing risk on a more effective basis;
- More effective management of risk that enables Customs to detect high-risk consignments;
- Improved controls along the international trade supply chain and make for better and more efficient allocation of Customs resources;
- Strengthened cooperation between Customs Administrations that enables Administrations to carry out controls earlier in the supply chain. For example, the Customs Administration at the country of exportation can conduct an inspection on behalf of the importing country’s Customs Administration;
- Mutual recognition of controls under certain circumstances which eliminates duplication and multiple reporting requirements.
Benefits to Business
- SAFE Framework takes account of, and is based on, modern international production and distribution models, thus it promotes international trade;
- Authorized Economic Operators will reap benefits, such as faster processing of goods by Customs, e.g. through reduced examination rates and expedited processing of their goods. This translates into savings in time and costs;
- Creation of one set of international standards helps to establish uniformity and predictability;
- Reduction of multiple and complex reporting requirements.
Learning Activities
Review the following and discuss their implications to a Freight Forwarder:
- Revised Kyoto Convention (RKC), 1999
- World Trade Organization (WTO) Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA)
- WCO SAFE Framework of Standards
Assignment
- Explain the various sources of Customs Laws in the East Africa Community.
- Describe any two similarities in the roles of the World Trade Organization and the World Customs Organization.
- Describe any two differences in the roles of the World Trade Organization and the World Customs Organization.
- Name some of the reform and modernization initiatives undertaken by the Customs Administration in your country, that are aligned to provisions of the Revised Kyoto Convention, 1999.
- Explain the importance of the WCO SAFE Framework of Standards to Traders
