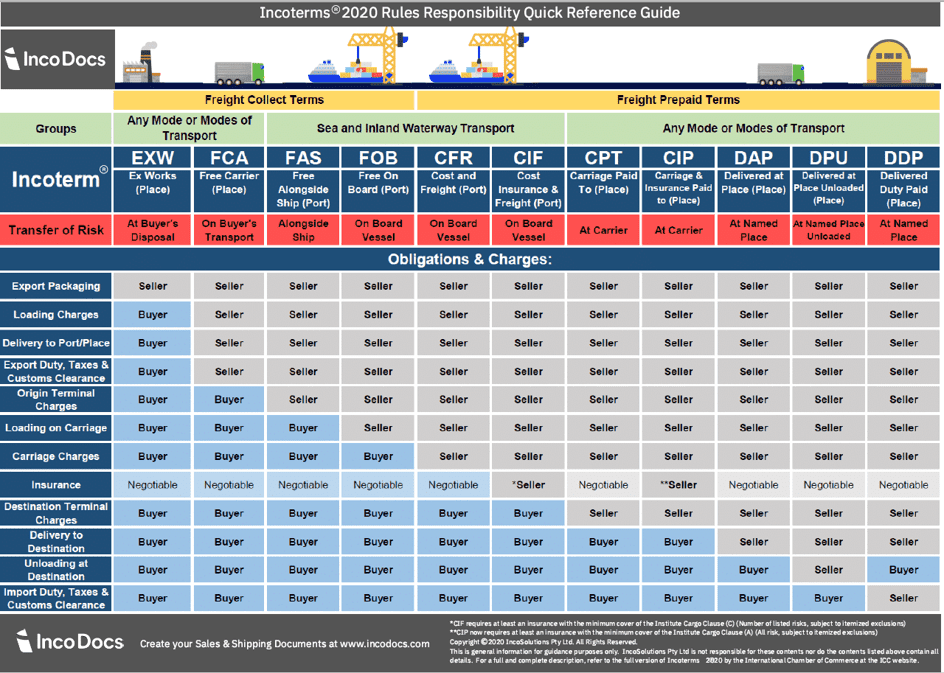
Rules for Sea and Inland Waterway Transport.
FAS – free alongside Ship (named port of shipment)
- The seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the vessel (e.g., on a quay or a barge) nominated by the buyer at the named port of shipment.
- The seller must clear the goods for export. It is suitable only for maritime transport but NOT for multimodal sea transport in containers.
- The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are alongside the ship, and the buyer bears all costs from that moment onwards
FOB – Free on Board (named port of shipment)
- The seller must load the goods on board the vessel nominated by the buyer.
- Cost and risk are divided when the goods are actually on board of the vessel.
- The seller must clear the goods for export.
- The buyer must instruct the seller the details of the vessel and the port where the goods are to be loaded, and there is no reference to, or provision for, the use of a carrier or forwarder.
- It is important that the shipment term in the Bill of Lading must carry the wording “Shipped on Board’ it must bear the signature of a transporter or carrier or his authorized representative with the date on which goods were “Boarded”.
- The buyer chooses the ship and pays freight.
- Transfer of expenses and risks is done once the goods passes ship’s rail
CFR – Cost and Freight (named port of destination)
- Seller must pay the costs and freight to bring the goods to the port of destination.
- However, risk is transferred to the buyer once the goods are loaded on the vessel.
- Maritime transport only and Insurance for the goods is NOT included.
- The risk of loss of or damage to the goods passes when the goods are on board the vessel.
- The seller must contract for and pay the costs and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination.
CIF – Cost, Insurance and Freight (named port of destination)
- “CIF “means” that the seller delivers when the goods pass the ship’s rail in the port of shipment risk passes to buyer when goods are delivered on board the ship by seller who pays transportation and insurance cost to destination port.
- This Term involves insurance with FOB price and ocean freight.
- The marine insurance is obtained by the exporter at his cost against the risk of loss or damage to the goods during the carriage.
- The CIF extends additional obligation to the seller for providing a maritime insurance against the risk of loss or damage to the goods.
- The buyer should ALSO take insurance cover.
- The buyer takes delivery of the goods from the carrier to the appointed port or destination but risks at port of origin.

Learning Activities
- An exporter from the East Africa region has approached you as a competent freight forwarder to advice on the best INCOTERM to use for exporting his cargo to the European market. Discuss as a group by providing various options considering that the exporter is in business of selling his goods and also making maximum profit.
- ABC KENYA LIMITED a Kenya based trading company in Nairobi dealing in various general merchandise is buying from their China based supplier the following goods on CIF Mombasa basis. All the containers are FCL with some to be delivered in a Nairobi ware house. The five containers are on one bill of lading number MSKU 0218543. Fifty percent of the cargo is for home use with the rest to be sold to Southern Sudan on DDP Juba terms.
- The five containers are each said to contain the following:
- 1X20 FCL STC Fire works
- 1X20 FCL STC 200 pcs Flat screen television
- 1X40 FCL STC Various types of shoes in different sizes
- 1X40 STC 200 pcs Un assembled motor bikes of different ratings
- 1X20 STC Wheat flour in 100 kg bags for re packaging in 2kg packages and branded
Required
1. What are the duties and responsibilities of ABC Kenya limited under the above INCOTERMS?
- Consider both duties and responsibilities of freight forwarders under CIF and DDP terms.
2. Describe the likely port charges for the above consignment
- The port charges should include all cargo related charges such as wharfage, cargo handling charges, removal charges and storage charges.
3. Describe the required type of ware housing and the requisite activities
- Consider aspect of bonded warehouses (for Juba consignment where duty is not paid), specialized warehouses (fireworks), sorting warehousing and distribution warehousing (for Nairobi based consignments).
1.During customs clearance at a CFS in Nairobi the customs officer chose not to verify 100% as he was exhausted. The CFS operator provided casual laborers for offloading and loading. The customs officer wrote a verification account (V/A) based on the parking list as seals were intact. The customs agent countersigned but upon arrival at the bonded warehouse on a shunting truck it was noted that 10 flat screens were missing, 5 were broken and 20 were a size smaller than what was ordered. As an experienced freight forwarder, you are required to advise on the following:
- Where the loss could have occurred?
- What steps should have been taken to avert the loss?
2.What parties shall ABC deal with in the process of port clearance and what will the role of each party be?
- What steps shall ABC take to ensure shipping line charges are minimized on the container?
- What precautions should ABC take when selling to Southern Sudan under the stated INCOTERMS above to ensure the company meets its obligations whilst minimizing risk and without making loss?
- What qualities should ABC look out for in a suitable forwarder for this business?
- Tallow Oil Pty an oil and gas exploration company is set to drill a new oil well site on the shores of Lake Albert in western Uganda. The area is remotely located. Tallow will require expert logistics advise to mobilize and have a rig on site. The lead time will be short in order to minimize costs (The cost of hiring the rig is USD 300,000 per day). This should however not compromise EHS (Environmental Health Safety) standards. They have contracted the services of M/S FINA Logistics Ltd to ensure the rig arrives on time, safely and at the right cost.
- Note:
- Cargo shall include:
- 1x20ft explosives
- out of gauge pieces
- items from different countries and suppliers under different incoterms
- Various small size drill bits that are urgent
- Various chemicals
- 2x40ft Frozen food stuff
- The contract value for these services is about USD 3 Million
Required:
- What advance preparation should FINA Logistics make to ensure it meets project expectations?
- How does FINA Logistics protect its interests in the process of execution of the contract?
- How should FINA Logistics effectively execute the contract?
- Degremonts Company Ltd the Contractor of lower Ruvu water project at Bagamoyo has ordered various types of pipes and pipe fittings from China for a project. The cargo tonnage is 5250 tones with the cbm of 8960. This cargo is to be cleared under donor funded project and according to the port of Dar es salaam regulations the cargo must be direct delivery from the ship. Degremonts contracted Kiwaepa International Company Ltd a freight and logistics firm to undertake clearance of the cargo at Dar-es-salaam port and transport the pipes to Bagamoyo site which is 60 km from Dar-es-salaam with 12KM comprising of rough and seasonal stretch.
Required:
- Prepare a quotation for clearance and transportation
- Consider Port Charges, shipping charges, customs clearance, processing exemption, inland transport to Bagamayo and handling cost
- Consider the bad 12km bad road /seasonal road since it may result into storing the pipes outside the port until the road is passable.
2. What steps should Kiwaepa International Company take to ensure that they get the right trucks to deliver the pipes?
- They must carefully study the packing list and stowage plan in order to get pipe dimensions for the suitable trucks.
Describe the various options to minimize the job costs and meet port discharging schedule.
- Consider option of hiring storage place next to the port for keeping pipes to avoid truck delay and ship demurrage costs.
- Consider available suitable trucks to run 24-hour operations without stowing pipes next to the port. In this case, should increase number of trucks and avoid traffic congestion.
Assignment
1.Explain the specific points where risk passes under the following terms
- CIF
- DPU
- FAS
- EXW
2.Explain the importance of using INCOTERMS in international business transaction between sellers and buyers of goods.
