Types/Classification of Containers
- Containers are classified based on material of construction, size and use.
- Classification based on material of construction
- Steel containers
- Aluminum containers
- GRP containers
Classification based on size
- Standard Containers are 20 or 40 feet long, 8 feet 6 inches high and 8 feet wide.
- High Cube Containers are 20 or 40 feet long, 9 feet 6 inches high and 8 feet wide.
- Super High Cube Containers have dimensions, which exceed the standard ISO sizes. The dimensions vary and may reach up to 53 feet long. These types of containers are used for transporting light but high-volume cargo and over height cargoes up to a maximum of 2.70 m tall.
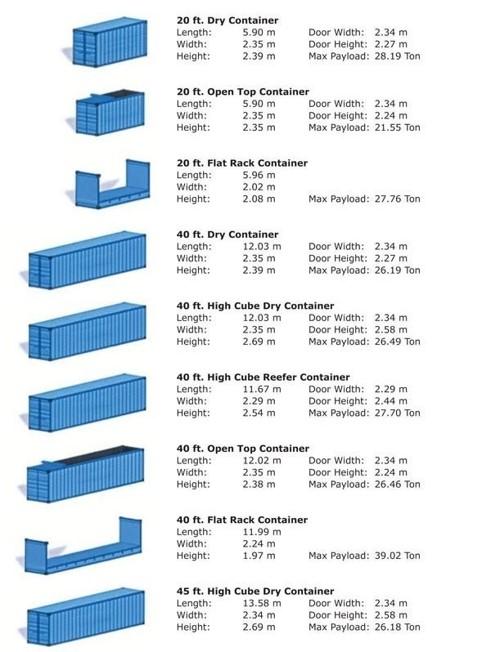

Classification based on use
- Dry Freight or General Cargo Containers
- It is enclosed and waterproof
- The frame and bottom cross members are made of steel.
- The sides and top are made of corrugated steel, aluminum or plywood with fiber glass coating.
- The floors are made of wood.
- At least one end wall has sealable doors.
- For ease of lifting, they are usually fitted with forklift pockets for handling when empty.
- They are used for all types of dry cargo.
- Dry containers are the most common type of container


- Ventilated Containers
- Used for the transportation of farm produce such as coffee, cocoa and tea.
- Ventilation is provided by openings in the top and bottom side rails.
- The openings prevent water ingress.
Thermal Containers
- These are used to carry cargoes requiring temperature control.
Reefer Containers
- Have insulated walls, doors, roof and floor, which limit the extent of temperature loss or gain.
- They are used for transporting perishable goods like meat, fruits and vegetables.
- An ISO shipping container is used for the shipment of temperature sensitive, perishable cargo such as meats, fruits and vegetables.
- Reefers generally come in 20’ and 40, and are commonly made from weathering steel known as ‘Cor-ten’ steel.
Insulated Containers
- An insulated or thermal container has a regulated temperature control that allows them to withstand a higher temperature.
- They are equipped with an electrical compliance (mechanical compressor) to cool or heat the air within the container.
Refrigerated Containers with Expendable refrigerant
- These use dry ice or liquefied gases. They do not require external power supply or fuel supply.
Mechanically refrigerated containers
- These use a refrigerating appliance (mechanical compressor) or absorption unit.
Heated Container
- This uses a heating appliance. Examples in east Africa are the containers for bitumen.
Refrigerated and heated container
- This uses a refrigerating appliance (mechanical or expendable refrigerant) and a heater.
Tank Containers
- Used for the carriage of bulk gases and liquids.
Dry Bulk Containers
- Used for carriage of dry solids in bulk without packaging such as grains and dry chemicals.
Open Top Containers
- These are general purpose containers with no rigid roof. They may have flexible or removable canvas cover.
Special Cargo Containers
- These containers are built for specific cargoes. They are also built to ISO specification.


Flat rack container
- With collapsible sides, these are like simple storage shipping containers where the sides can be folded so as to make a flat rack for shipping of a wide variety of goods.


Tank Containers
- Half Height Containers
- Half-height shipping containers are designed for transporting bulk cargo that is heavy and dense. These are good for transporting goods such as coal and stones, so they are perfect for use in the mining industry.


Car Carriers
- Car carriers are container storage units made especially for shipment of cars over long distances. They come with collapsible sides that help a car fit snugly inside the containers without the risk of being damaged or moving from the spot.


